Subscribe
Northwell Health, New York State’s largest healthcare provider, recently launched a large language model tool that it is encouraging doctors and clinicians to use for translation, sensitive patient data, and has suggested it can be used for diagnostic purposes, 404 Media has learned. Northwell Health has more than 85,000 employees.
An internal presentation and employee chats obtained by 404 Media shows how healthcare professionals are using LLMs and chatbots to edit writing, make hiring decisions, do administrative tasks, and handle patient data.
In the presentation given in August, Rebecca Kaul, senior vice president and chief of digital innovation and transformation at Northwell, along with a senior engineer, discussed the launch of the tool, called AI Hub, and gave a demonstration of how clinicians and researchers—or anyone with a Northwell email address—can use it.
AI Hub “uses [a] generative LLM, used much like any other internal/administrative platform: Microsoft 365, etc. for tasks like improving emails, check grammar and spelling, and summarizing briefs,” a spokesperson for Northwell told 404 Media. “It follows the same federal compliance standards and privacy protocols for the tools mentioned on our closed network. It wasn't designed to make medical decisions and is not connected to our clinical databases.”
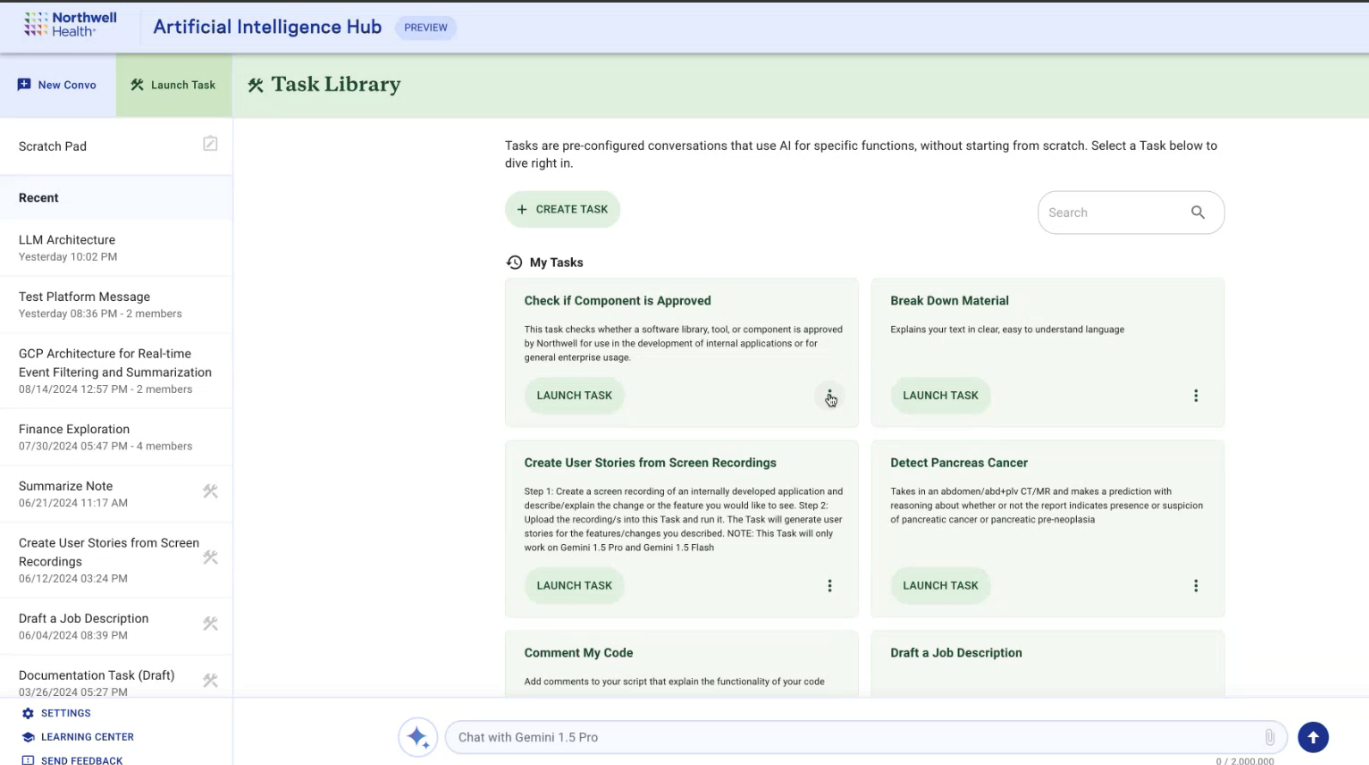
But the presentation and materials viewed by 404 Media include leadership saying AI Hub can be used for "clinical or clinical adjacent" tasks, as well as answering questions about hospital policies and billing, writing job descriptions and editing writing, and summarizing electronic medical record excerpts and inputting patients’ personally identifying and protected health information. The demonstration also showed potential capabilities that included “detect pancreas cancer,” and “parse HL7,” a health data standard used to share electronic health records.
The leaked presentation shows that hospitals are increasingly using AI and LLMs to streamlining administrative tasks, and shows that some are experimenting with or at least considering how LLMs would be used in clinical settings or in interactions with patients.

